| FOOT DISORDERS - Shin Splints |
"Shin splints" is an outdated term variously used to describe pain in the lower leg. It is, however, still in common use today.
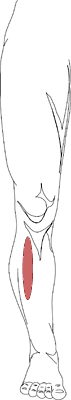
Medial shin splints are defined as pain in the lower aspect of the medial (inside) tibia 3 to 12 centimeters above the tip of the medial ankle. There is tenderness to touch in this area along the posterior (back) aspect of the tibia bone. The muscles and tendons are inflamed as well as the membrane (periosteum) around the bone. This is where the medial leg musculature attaches to the bone. This is a repetitive stress (overuse) injury. The most frequently involved muscle is the Posterior tibial muscle, but the Flexor digitorum longus and the Flexor hallucis longus muscles may also be involved.
Medial shin splints are common in athletes who are increasing their level of activity or its duration. It may also occur during transitioning from one sport to another
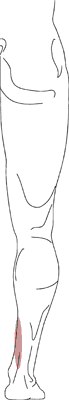
Anterior shin splints are soft tissue injury at the origin on the anterior tibial muscle along the anterior-lateral (front towards the outside) aspect of the lower leg. There is tenderness to touch in this area. The muscle and its attachment to the bone are inflamed. Like Medial Shin Splints, this is a repetitive stress (overuse) injury.
Anterior shin splints frequently occur in athletes beginning a weight bearing exercise program. Overtraining of more seasoned athletes is sometimes responsible.
Foot orthotic devices can provide support for
stressed joints and soft tissues. They are often constructed to increase shock
absorption. The redistribution of weight relieves stress on the metatarsals.
Generally, custom-made semi-rigid or semi-flexible functional posted orthotics
are most effective for this foot type. They often include shock absorbing
material in the arch. These devices are prescribed based on a thorough
biomechanical examination by a qualified podiatrist. Orthotic therapy is very
effective for patients with this foot type. Over-the-counter arch supports may
be helpful for mild cases, but they are often a poor fit for persons with this
condition.

